Abstract
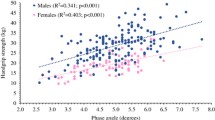
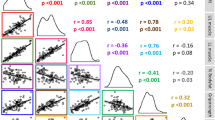
In this paper the assessment of the relationship between chest expansion with maximal inspiratory (MIP) and expiratory pressures (MEP) in primary fibromyalgia (FM) syndrome is discussed. Chest expansion (CE) measurements, spirometric values, and MIP and MEP values in 30 female patients with primary FM are compared with 29 healthy age-matched female controls. Patients with FM had lower CE, MEP and MIP values than controls. CE correlated significantly with MIP and MEP values. There was no significant difference between groups in spirometric values. Our results indicate that patients with FM have impaired respiratory muscle strength, and measurement of CE may be a useful clinical parameter. Despite its limitations CE may reflect respiratory muscle strength. It is worth following up these data in a wider and controlled series, with ancillary tests in addition to the MIP and MEP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 January 2001 / Accepted: 13 July 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozgocmen, S., Cimen, O. & Ardicoglu, O. Relationship between Chest Expansion and Respiratory Muscle Strength in Patients with Primary Fibromyalgia. Clin Rheumatol 21, 19–22 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100670200005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100670200005