Abstract
Background: In the intensive care unit, therapists utilize various tools to assess and monitor respiratory illness; those tools are mathematical models such as the ratio of arterial oxygen tension to inspired oxygen fraction, arterial/alveolar oxygen tension ratio, alveolar-arterial oxygen tension difference, respiratory index, oxygen index and oxygen saturation index. However, evidence reported that some pulmonary physiological factors were not integrated into the calculation of those models. Therefore, this research aimed to demonstrate the variation in those models within a short period within critical care settings.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was carried out in ICU at tertiary care center in Saudi Arabia between 2017–2019. Adult patients who have been admitted to the ICU and placed on the mechanical ventilation > 24 h were included. From the medical file of each patient, data on the mechanical ventilator setting and ABG results were extracted. Then, two different arterial blood gas samples were selected within a mean of 120 min based on patient-specific needs for one day. Continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviation (SD), categorical variables as frequencies and percentages. The coefficient of variation percent [(CV%) = SD/mean] was calculated and Institutional Review Board approval was obtained (IRB:SP20089R).
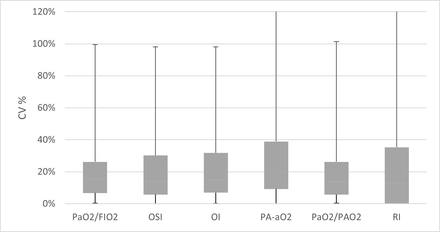
Results: A total of 211 intubated ICU patients were included in this study. The mean (SD) age of the study population was 57 (19.62), and 33% were female. The average CV% for all mathematical models report a degree of variation between (14%–30%). The mean CV% for PaO2/FIO2 and PaO2/ PaO2 was 14% which consider a low variation compared to the RI in which the mean CV% was 30%.
Conclusions: the finding of this study indicates the need to adopt a new model that integrate pulmonary physiological factors mathematically to represent a real lung condition. This will help alongside with the other oxygen indices in assessing the severity of respiratory illness.
Footnotes
Commercial Relationships: None
- Copyright © 2021 by Daedalus Enterprises