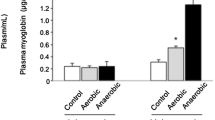
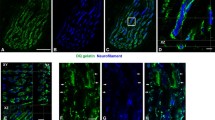
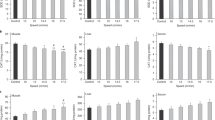
Summary
Adult, untrained NMRI mice were exhausted on a motor-driven treadmill by an intermittent-type running programme. Serial cryostate sections for the staining of NADH-tetrazolium reductase, β-glucuronidase, β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, and β-glycerophosphatase activities and for making hematoxylin-eosin staining were cut from m. quadriceps femoris 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, and 15 days after physical exhaustion. A strong increase in the activities of β-glucuronidase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, was observed 7 days after exhaustion and the activity changes, which were similar for the both glycosidases, were more prominent in the highly oxidative red compared to less oxidative white fibres. Activity granules were more numerous in the perinuclear than the interfibrillar area of red fibres. Spots were arranged like longitudinal chains between myofibrils. Activity in connective tissue was usually observed only in animals exhausted 3–7 days earlier. Simultaneous activity in fibres exceeded that in connective tissue β-Glycerophosphatase activity was not, by the method used, seen in histologically “healthy” or normal-looking fibres. in samples taken 2–5 days after exhaustion some degenerating and necrotic fibres were observed. Inflammatory reaction was also observed being at its strongest five days after loading when mononuclear cells were seen inside necrotic fibres. The number of regenerating muscle cells was most abundant 7 days after exhaustion. It is suggested that temporary hypoxia, which accompanies exhaustive physical exercise in skeletal muscle, upsets the energy metabolism and homeostasis of fibres and causes the observed histological and histochemical alterations, which posses features typical of both lethal and sublethal acute cell injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altland, P.D., Highman, B.: Effects of exercise on serum enzyme values and tissues of rats. Am. J. Physiol. 201, 393–395 (1961)
Arcangeli, P., Digiesi, V., Masala, B., Serra, M.V., Congiu, A.: Metabolism of skeletal muscle following incomplete ischemia. Angiology 24, 114–122 (1973)
Arstila, A.U., Hirsimäki, P., Trump, B.F.: Studies on subcellular pathophysiology of sublethal chronic cell injury. Beitr. Pathol. 152, 211–242 (1974)
Bird, J.W.C.: Skeletal muscle lysosomes. Front. Biol. 43, 75–109 (1975)
Boström, S., Fahlen, M., Hjalmarson, A., Johansson, R.: Activities of rat muscle enzymes after acute exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 90, 544–554 (1974)
Bowers, W.D., Hubbard, R.W., Smoake, J.A., Damm, R.C., Nelson, E.: Effects of exercise on the ultrastructure of skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 227, 313–316 (1974)
Canonico, P.G., Bird, J.W.C.: Lysosomes in skeletal muscle tissue. Zonal centrifugation evidence for multiple cellular sources. J. Cell. Biol. 45, 321–333 (1970)
Chayen, J., Bitensky, L., Butcher, R.: Practical histochemistry. pp. 155–159. New York: John Wiley & Son, 1973
Christie, N.K., Stoward, P.J.: A cytochemical study of acid phosphatase in dystrophic hamster muscle. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 58, 219–234 (1977)
Gale, J.B.: Mitochondrial swelling associated with exercise and method of fixation. Med. Sci. Sports 6, 182–187 (1974)
Gollnick, P.D., King, D.W.: Effect of exercise and training on mitochondria of rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 216, 1502–1509 (1969)
Haljamäe, H., Enger, E.: Human skeletal muscle energy metabolism during and after complete torniquet ischemia. Ann. Surg. 182, 9–14 (1975)
Hecht, A., Schumann, H.-J., Kunde, D.: Histologische und enzymhistochemische Befunde an Skelettmuskel der untrainierten Ratte nach intensiver physischer Belastung. Med. Sport XB 270–274 (1975)
Henley, K.S., Mich, A.A., Schmidt, E., Schmidt, F.W.: Serum enzymes. Clin. Sci. 174, 119–123 (1960)
Highman, B., Altland P.D.: Effects of exercise and training on serum enzyme and tissue changes in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 205, 162–166 (1963)
Hirsimäki, Y., Vihko, V., Ajiduah, A., Arstila, A.U.: Post mortem changes in red and white skeletal muscle ultrastructure and in the activities of some enzymes of energy metabolism and lysosomes in untrained and trained mice. In: Hänninen, O. & Harri, M. (Ed.) Physical performance and muscle metabolism, No 57, pp. 201–221. Somero: The Finnish. Society for Research in Sport and Physical Education 1978
Körge, P., Viru, A.: Water and electrolyte metabolism in skeletal muscle of exercising rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 31, 1–4 (1971)
Linge van, B.: The response of muscle to strenuous exercise. J. Bone Joint Surg. 44, 711–721 (1962)
Lojda, Z., Gutmann, E.: Histochemistry of some acid hydrolases in striated muscle of the rat. Histochemistry 49, 337–342 (1976)
Manolov, S., Ovtscharoff, W.: Ultrastructural changes in the muscle cells of denervated muscles of rat. Z. Mikrosk. Anat. Forsch. 88, 726–744 (1974)
Maskrey, P., Pluskal, M.G., Harris, J.B., Pennington, R.J.T.: Studies on increased acid hydrolase activities in denervated muscle. J. Neurochem. 28, 403–409 (1977)
Max, S.R., Mayer, R.F., Vogelsang, L.: Lysosomes and disuse atrophy of skeletal muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 146, 273–232 (1971)
Mäkitie, J., Teräväinen, H.: Histochemical studies of striated muscle after temporary ischemia in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 37, 101–110 (1977)
Novikoff, A.B., Shin, W., Drucker, J.: Mitochondrial localization of oxidative enzymes. Staining results with two tetrazolium salts. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 47–61 (1961)
Pearse, A.G.E.: Histochemistry, theoretical and applied. p. 730. London: J. & A. Churchill 1968
Pilström, L., Vihko, V., Åström, E., Arstila, A.U.: Activities of acid hydrolases in skeletal muscle of untrained, trained and detrained mice of different ages. Acta Physiol. Scand., in press (1978)
Reznik, M.: Current concepts of skeletal muscle regeneration. In: Pearson, C.M. & Mostofi, F.K. (Ed.) The Striated Muscle, pp. 185–225. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins 1973
Sanders, T.M., Bloor, C.M.: Effects of endurance exercise on serum enzyme activities in the dog, pig and man. Proc. Soc. exptl. Biol. Med. 148, 823–828 (1975)
Schiaffino, S., Hanzlikova, V.: Studies on the effect of denervation in developing, muscle. II. The lysosomal system. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 39, 1–14 (1972)
Schumann, H.J.: Überlastungsnekrosen der Skelettmuskulatur nach experimentellem Laufzwang. Zbl. allg. Pathol. 116, 181–190 (1972)
Shannon, A.D.: A postcoupling method for the demonstration of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase in unfixed frozen tissue sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 424–430 (1975)
Shannon, A.D., Adams, E.P., Courtice, F.C.: The lysosomal enzymes acid phosphatase and β-glucuronidase in muscle following a period of ischemia. Austr. J. exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 52, 157–171 (1974)
Shannon, A.D., Courtice, F.C.: The lysosomal enzyme N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase in rabbit muscle following a period of ischemia. Pathology 7, 25–33 (1975)
Siest, G., Galteau, M.M.: Variations in plasmatic enzymes during exercise. Enzymology 17, 179–195 (1974)
Simonson, E.: Physiology of work capacity and fatigue. Illinois: Charles C. Thomas 1971
Terjung, R.L., Baldwin, K.M., Mole, P.A., Klinkerfuss, G.H., Holloszy, J.O.: Effect of running to exhaustion on skeletal muscle mitochondria: a biochemical study. Am. J. Physiol. 223, 549–554 (1972)
Trump, B.F., Laiho, K.A., Mergner, W.J., Arstila, A.U.: Studies on the subcellular pathophysiology of acute lethal cell injury. Beitr. Pathol. 152, 243–271 (1974)
Vihko, V., Arstila, A.U.: Ultrastructural mitochondrial changes in mouse skeletal muscle after forced exhaustive running exercise. IRCS, Med. Sci. 2, 1144 (1974a)
Vihko, V., Hirsimäki, Y., Arstila, A.U.: High β-glucuronidase activity in crude skeletal muscle homogenates, of dynamically trained mice. IRCS, Med. Sci. 2, 1147 (1974b)
Vihko, V., Hirsimäki, Y., Arstila, A.U.: Effect of acute and prolonged exercise on the activities of acid hydrolases in mouse skeletal muscle. In: Hänninen, O. & Harri, M. (Ed.) Physical performance and muscle metabolism, No 57, pp. 112–120, Somero: The Finnish Society for Research in Sport and Physical Education 1978a
Vihko, V., Salminen, A., Rantamäki, J.: Acid hydrolase activity in red and white skeletal muscle of mice during two-week period following exhaustive exercise. Pfluegers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. (1978b)
Weinstock, I.M., Iodice, A.A.: Acid hydrolase activity in muscular dystrophy and denervation atrophy. In: Dingle, J.T. & Fell, H.B. (Ed.): Lysosomes in Biology and Pathology, Vol. I, pp. 450–468. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1969
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vihko, V., Rantamäki, J. & Salminen, A. Exhaustive physical exercise and acid hydrolase activity in mouse skeletal muscle. Histochemistry 57, 237–249 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00492083
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00492083