Abstract
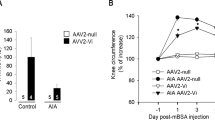
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic and debilitating autoimmune disease of unknown etiology, characterized by chronic inflammation in the joints and subsequent destruction of the cartilage and bone. We describe here a new strategy for the treatment of arthritis: administration of the neuropeptide vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Treatment with VIP significantly reduced incidence and severity of arthritis in an experimental model, completely abrogating joint swelling and destruction of cartilage and bone. The therapeutic effect of VIP was associated with downregulation of both inflammatory and autoimmune components of the disease. Our data indicate VIP as a viable candidate for the development of treatments for RA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldmann, M., Brennan, F.M. & Maini, R.N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 14, 397–440 (1996).
Mauri, C., Williams, R.O., Walmsley, M. & Feldmann, M. Relationship between Th1/Th2 cytokine patterns and the arthritogenic response in collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 1511–1520 (1996).
Doncarli, A., Stasiuk, L.M., Fournier, C. & Abehsira-Amar, O. Conversion in vivo from an early dominant Th0/Th1 response to a Th2 phenotype during the development of collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 27, 1451–1460 (1997).
Joosten, L.A. et al. Role of interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 40, 249–260 (1997).
Walmsley, M. et al. Interleukin-10 inhibition of the progression of established collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 39, 495–503 (1996).
Horsfall, A.C. et al. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis by continuous administration of interleukin-4. J. Immunol. 159, 5687–5696 (1997).
Pozo, D. et al. Immunobiology of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Immunol. Today 21, 7–11 (2000).
Delgado, M., Leceta, J., Gomariz, R.P. & Ganea, D. VIP and PACAP stimulate the induction of Th2 responses by upregulating B7.2 expression. J. Immunol. 163, 3629–3635 (1999).
Delgado, M., Munoz-Elias, E.J., Gomariz, R.P. & Ganea, D. VIP and PACAP inhibit IL-12 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Subsequent effect on IFNγ synthesis by T cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 96, 167–181 (1999).
Myers, L.K., Rosloniec, E.F., Cremer, M.A. & Kang, A.H. Collagen-induced arthritis, an animal model of autoimmunity. Life Sci. 61, 1861–1872 (1997).
Delgado, M., Munoz-Elias, E.J., Martinez, C., Gomariz, R.P. & Ganea, D. VIP and PACAP-38 modulate cytokine and nitric oxide production in peritoneal macrophages and macrophage cell lines. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 897, 401–420 (1999).
O'Garra, A.O. Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immunity 8, 275–287 (1998).
Seki, N. et al. Type II collagen-induced murine arthritis induction and perpetuation of arthritis require synergy between humoral and cell-mediated immunity. J. Immunol. 140, 1477–1487 (1988).
Taylor, P.C., Zyberk, C.P. & Maini, R.N. The role of the B cells in the adoptive transfer of collagen-induced arthritis from DBA/1 (H-2q) to SCID (H-2d) mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 763–771 (1995).
Butler, D.M., Malfait, A.M., Maini, R.N., Brennan, F.M. & Feldmann, M. Anti-IL-12 and anti-TNF antibodies synergistically suppress the progression of murine collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 2205–2212 (1999).
Malfait, A.M. et al. Blockade of interleukin 12 during the induction of collagen-induced arthritis markedly attenuates the severity of the arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 111, 377–386 (1998).
Brennan, F.M., Chantry, D., Jackson, A., Maini, R.N. & Feldmann, M. Inhibitory effect of TNFa antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2, 244–251 (1989).
Woessner, J.F. Jr. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 5, 2145–2154 (1991).
Gourlet, P. et al. Development of high affinity selective VIP1 receptor agonists. Peptides 18, 1539–1546 (1998).
Xia, M., Sreedharan, S.P., Bolin, D.R., Gaufo, G.O. & Goetzl, E.J. Novel cyclic peptide agonist of high potency and selectivity for the type II vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 281, 629–638 (1997).
Moro, O. & Lerner, E.A. Maxadilan, the vasodilator peptide from sand flies, is a specific pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide type I receptor agonist. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 966–974 (1996).
Moreland, L.W. et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human TNF receptor (p65)-Fc fusion protein. N. Engl. J. Med. 337, 141–147 (1997).
Elliot, M.J. et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to TNFα. Arthritis Rheum. 36, 1681–1689 (1993).
Watt, I. & Cobby, M. Recombinant human IL-1 receptor antagonist (rhIL-1ra) reduces the rate of joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Arthritis Rheum. 39, S123 (1996).
Dinant, H.J. & Dijkmans, B.A.C. New therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. World Sci. 21, 49–59 (1999).
Takeba, Y., Suzuki, N., Kaneko, A., Asai, T. & Sakane, T. Evidence for neural regulation of inflammatory synovial cell functions by secreting calcitonin gene-related peptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 2418–2429 (1999)
Butler, D.M. et al. DBA/1 mice expressing the human TNFα transgene develop a severe, erosive arthritis: characterization of the cytokine cascade and cellular composition. J. Immunol. 159, 2867–2876 (1997).
Delgado, M. et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide inhibit TNFα transcriptional activation by regulating NF-κB and CREB/c-Jun. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 31427–31436 (1998).
Delgado, M., Munoz-Elias, E.J., Gomariz, R.P. & Ganea, D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide prevent inducible nitric oxide synthase transcription in macrophages by inhibiting NFκB and IFN regulatory factor 1 activation. J. Immunol. 162, 4685–4696 (1999).
Espevik, T. & Nissen-Meyer, J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J. Immunol. Methods 95, 99–105 (1989).
Robbins, J.R., McGuire, P.G., Wehrle-Haller, B. & Rogers, S.L. Diminished matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) in ectomesenchyme-derived tissue of the Patch mutant mouse: regulation of MMP-2 by PDGF and effects on mesenchymal cell migration. Dev. Biol. 212, 255–263 (1999).
Seetharaman, R. Mora, A.L., Nabozny, G., Boothby, M. & Chen, J. Essential role of T-cell NF-κB activation in collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 163, 1577–1583 (1999).
Kusaba, M., Honda, J., Fukuda, T. & Oizumi, K. Analysis of type 1 and type 2 T cells in synovial fluid and peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 25, 1466–1471 (1998)
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Robberecht for the VPAC1 agonist and antagonist; D. Bolin and A. Welton for the VPAC2 agonist Ro 25-1553; and E. Lerner for the PAC1 agonist maxadilan. This work was supported by grant PM98-0081, and by the postdoctoral fellowships from the Spanish Department of Education and Science (M.D.) and the Autonomic Community of Madrid (C.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delgado, M., Abad, C., Martinez, C. et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease. Nat Med 7, 563–568 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/87887
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/87887
This article is cited by
-
The neuropeptide PACAP alleviates T. gondii infection-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal impairment
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2022)
-
A shedding soluble form of interleukin-17 receptor D exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis through facilitating TNF-α-dependent receptor clustering
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)
-
Chebulinic acid is a safe and effective antiangiogenic agent in collagen-induced arthritis in mice
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2020)
-
Activation of Th lymphocytes alters pattern expression and cellular location of VIP receptors in healthy donors and early arthritis patients
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide gene polymorphisms, associated with its serum levels, predict treatment requirements in early rheumatoid arthritis
Scientific Reports (2018)