Abstract
BACKGROUND: The use of neurally-adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) during noninvasive ventilation (NIV) results in better patient-ventilator interaction. Whether this improves clinical outcomes lacks dedicated study.
METHODS: In this randomized controlled trial, we compared NAVA with PSV for delivering NIV in consecutive subjects with de novo acute respiratory failure. The primary outcomes were NIV failure rates and 28-d mortality. The secondary outcomes were asynchrony index, NIV-related complications, and others.
RESULTS: We enrolled 100 subjects (50 subjects each for NAVA and PSV, 60% male) with a mean ± SD age of 56.7 ± 12 y. There was no difference in NIV failure rates (30% vs 32%, P = .83) and 28-d mortality rates (18% vs 34%, P = .07) between the NAVA and PSV arms, respectively. The median asynchrony index was significantly lower with NAVA (6.7 vs 44.8, P < .001). The use of NAVA significantly reduced NIV-related complications (32% vs 58%, P = .01). In a post hoc analysis, the use of NAVA significantly reduced the 28-d mortality in subjects with COPD exacerbation.
CONCLUSIONS: The use of NAVA during NIV did not improve NIV failure rate or 28-d mortality in subjects with acute respiratory failure. However, patient-ventilator asynchrony and NIV-related complications were reduced with NAVA.
Trial registry: www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03271671)
- respiratory failure
- mechanical ventilation
- noninvasive ventilation
- pressure support ventilation
- neurally adjusted ventilatory assist
- bi-level positive airway pressure
Introduction
Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is an important treatment option in the management of acute respiratory failure (ARF).1 The success of NIV depends on several factors, including the etiology of respiratory failure, the use of an appropriate interface, the provision of humidification, and patient-ventilator synchrony.2 patient-ventilator asynchrony is an important cause of NIV failure because it leads to increased work of breathing that may be associated with patient discomfort and prolonged duration of mechanical ventilation.3 Unfortunately, patient-ventilator asynchrony is common during NIV.4 Pressure support ventilation (PSV), the most commonly used mode of NIV, is associated with a high degree of patient-ventilator asynchrony.4 Although PSV enables the patient to influence the breathing pattern, ineffective or auto-triggering causes patient-ventilator asynchrony and results in NIV failure.4
Neurally-adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) is a ventilatory mode that utilizes the electrical activity of the diaphragm (EAdi) to mechanically ventilate the patient.5 During NAVA, the amount of pressure support delivered during each breath is proportional to the EAdi, which is a measure of the neural drive to the diaphragm.6 NAVA has been shown to reduce patient-ventilator asynchrony,7 avoid overassistance, decrease intrinsic PEEP, and minimize wasted effort.8 However, no study to date has primarily investigated clinical outcomes with the use of NAVA during NIV in ARF. We hypothesized that the use of NAVA would be associated with reduced NIV failure compared to PSV due to better patient-ventilator interaction. In this article, we compare the clinical outcomes between NAVA and PSV in subjects with ARF requiring NIV.
QUICK LOOK
Current knowledge
The use of neurally-adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) during noninvasive ventilation (NIV) results in better patient-ventilator interaction. Whether this improves clinical outcomes is not known.
What this paper contributes to our knowledge
The use of NAVA to deliver NIV did not improve NIV failure rates or 28-d mortality. However, NAVA during NIV reduced NIV-related complications and produced better patient-ventilator interaction compared to pressure support ventilation. In a post hoc analysis, NAVA during NIV reduced 28-d mortality in subjects with COPD exacerbation.
Methods
Setting
This was an investigator-initiated, single-center, randomized controlled trial conducted between July 2017 and June 2019 in the respiratory ICU of the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research. The respiratory ICU is an 8-bed unit where we treat medically ill patients. The Institutional Ethics Review Committee approved the study protocol (TRB2447/1/7/17). Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects or their next of kin.
Study Subjects
Consecutive patients ≥ 18 y and ≤ 90 y requiring NIV for ARF or for prevention of postextubation respiratory failure (preemptive NIV) were included in this study. The diagnosis of ARF was made in patients with new or worsening dyspnea of < 1-week duration, and at least 2 of the following: breathing frequency > 30 breaths/min; arterial blood gas analysis showing  < 60 mm Hg with or without
< 60 mm Hg with or without  > 45 mm Hg (and pH < 7.35);
> 45 mm Hg (and pH < 7.35);  < 300 or; use of accessory muscles of respiration or paradoxical respiration. Preemptive NIV was administered to patients who were deemed to have a high risk of developing respiratory failure after extubation based on standard criteria (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).9 Patients with severe ARDS (
< 300 or; use of accessory muscles of respiration or paradoxical respiration. Preemptive NIV was administered to patients who were deemed to have a high risk of developing respiratory failure after extubation based on standard criteria (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).9 Patients with severe ARDS ( ≤ 100), > 2 organ failures, established postextubation respiratory failure, or contraindications to the use of NIV were excluded (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). Because this was a pilot study, we enrolled a convenience sample of 100 subjects (NAVA = 50, PSV = 50).
≤ 100), > 2 organ failures, established postextubation respiratory failure, or contraindications to the use of NIV were excluded (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). Because this was a pilot study, we enrolled a convenience sample of 100 subjects (NAVA = 50, PSV = 50).
Randomization
Consecutive subjects meeting the inclusion criteria were sequentially randomized 1:1 to either the NAVA or the PSV arm at ICU admission. The randomization sequence was computer-generated with blocks of 4, and the sequential numbers were placed in opaque, sealed envelopes. The envelopes were opened by ICU physicians who were not directly involved with the study or with the analysis of the results. Blinding of the ICU physicians was not possible because the ventilatory strategies were intrinsically different. However, the investigators analyzing the results were blinded to the assignment of the group.
Study Procedure
NIV was administered in both arms using the Servo-i ventilator (Maquet, Getinge Group, Solna, Sweden). We delivered NIV through an oronasal mask (UltraMirage, ResMed, Sydney, Australia) of appropriate size. Subjects were allowed intermittent periods off NIV for eating or expectoration of respiratory secretions. During such periods, they were given oxygen through nasal cannula, with a target  of 89–92%. Subjects in both study groups received standard medical care (eg, enteral nutrition, deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis, stress ulcer prophylaxis) as per the existing ICU protocol, in addition to the treatment specific to the underlying clinical condition. We did not use sedation during NIV.
of 89–92%. Subjects in both study groups received standard medical care (eg, enteral nutrition, deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis, stress ulcer prophylaxis) as per the existing ICU protocol, in addition to the treatment specific to the underlying clinical condition. We did not use sedation during NIV.
PSV Mode.
Subjects randomized to PSV mode were ventilated with an initial pressure support of 6 cm H2O above PEEP, which was adjusted in steps of 2 cm H2O every 15 min to achieve a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg ideal body weight, breathing frequency < 30 breaths/min, and relief from dyspnea. PEEP was commenced at 5 cm H2O and was titrated along with  to achieve the target
to achieve the target 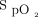 of 89–92%. A minimum pressure difference of 4 cm H2O between pressure support and PEEP was always maintained. The maximum pressure support and PEEP allowed in the study were 20 cm H2O and 10 cm H2O, respectively.
of 89–92%. A minimum pressure difference of 4 cm H2O between pressure support and PEEP was always maintained. The maximum pressure support and PEEP allowed in the study were 20 cm H2O and 10 cm H2O, respectively.
NAVA Mode.
NAVA was administered as previously described (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).10 Briefly, subjects in the NAVA arm were ventilated on PSV mode initially for 30 min for stabilization, and then they were switched to NAVA preview mode. The NAVA level was set to achieve a pressure support similar to the initial PSV mode, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. PEEP and  were adjusted like in the PSV arm. EAdi trigger was initially set to 0.5 μV and was adjusted (if needed) as per clinical requirements. Subsequently, the NAVA level was increased by 0.2 cm H2O/μV every 15 min to achieve a breathing frequency < 30 breaths/min and a tidal volume of 6 mL/Kg ideal body weight. The maximum NAVA level allowed was 3 cm H2O/µV, which corresponds to a pressure support level of 25–30 cm H2O.11,12
were adjusted like in the PSV arm. EAdi trigger was initially set to 0.5 μV and was adjusted (if needed) as per clinical requirements. Subsequently, the NAVA level was increased by 0.2 cm H2O/μV every 15 min to achieve a breathing frequency < 30 breaths/min and a tidal volume of 6 mL/Kg ideal body weight. The maximum NAVA level allowed was 3 cm H2O/µV, which corresponds to a pressure support level of 25–30 cm H2O.11,12
Baseline Assessment and Monitoring.
At ICU admission, clinical details including etiology of respiratory failure and significant comorbidities were collected (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). We monitored breathing frequency, heart rate, blood pressure, Glasgow coma score,  , signs of respiratory fatigue (eg, respiratory alternans, paradoxical breathing), and fit of mask every 15 min for the initial 4 h. Arterial blood gas analysis was performed at the initiation of NIV and repeated at 1, 2, 4, 12, and 24 h after the initiation of NIV, at study end point, and at discharge from the ICU.
, signs of respiratory fatigue (eg, respiratory alternans, paradoxical breathing), and fit of mask every 15 min for the initial 4 h. Arterial blood gas analysis was performed at the initiation of NIV and repeated at 1, 2, 4, 12, and 24 h after the initiation of NIV, at study end point, and at discharge from the ICU.
Measurement of Asynchrony.
A NAVA catheter was inserted in each subject to continuously measure EAdi and to note the peak and minimum EAdi values over each ventilator cycle.10 The following asynchronies were checked and recorded as the number of events/minute: ineffective efforts, trigger delay, double-triggering, auto-triggering, premature cycling, delayed cycling (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). Asynchrony index was calculated as described previously13; asynchrony index > 10% was termed as severe.
Weaning.
Weaning from PSV and NAVA was performed using predetermined criteria.14 In the PSV group, once the subject’s clinical condition stabilized, pressure support was reduced in steps of 2 cm H2O every 2 h. In the NAVA group, once the EAdi started to decline or remained unchanged with stable tidal volumes, the NAVA level was decreased in steps of 0.2 cm H2O/µV every 2 h. Simultaneously, PEEP was reduced in both groups by decrements of 1 cm H2O. Care was taken to maintain  > 88% at
> 88% at 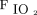 ≤ 0.3, breathing frequency ≤ 30 breaths/min, and tidal volume of 6–8 mL/kg ideal body weight. If any of the aforementioned conditions were not met, or the EAdi signal increased disproportionately (only in the NAVA group) at any time during the downtitration, the settings of the previous step were retained. In the PSV group, reduction of pressure support and PEEP were continued in this manner until a pressure support of ≤ 12 cm H2O and PEEP of ≤ 5 cm H2O was reached. In the NAVA group, reduction of NAVA level and PEEP was continued until a peak pressure of ≤ 12 cm H2O and PEEP of ≤ 5 cm H2O at a NAVA level of < 0.5 cm H2O/µV was reached. Once the subject was comfortable on these settings for 4–6 h, the subject was taken off NIV and connected to an air-entrainment mask with
≤ 0.3, breathing frequency ≤ 30 breaths/min, and tidal volume of 6–8 mL/kg ideal body weight. If any of the aforementioned conditions were not met, or the EAdi signal increased disproportionately (only in the NAVA group) at any time during the downtitration, the settings of the previous step were retained. In the PSV group, reduction of pressure support and PEEP were continued in this manner until a pressure support of ≤ 12 cm H2O and PEEP of ≤ 5 cm H2O was reached. In the NAVA group, reduction of NAVA level and PEEP was continued until a peak pressure of ≤ 12 cm H2O and PEEP of ≤ 5 cm H2O at a NAVA level of < 0.5 cm H2O/µV was reached. Once the subject was comfortable on these settings for 4–6 h, the subject was taken off NIV and connected to an air-entrainment mask with 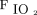 adjusted to maintain
adjusted to maintain  of 89–92%.
of 89–92%.
Outcomes
All subjects were followed until death or up to 3 months after hospital discharge, whichever was earlier. The primary outcomes were NIV failure and 28-d mortality. NIV was deemed to have failed if one of the following occurred: (i) endotracheal intubation during or within 48 h of NIV discontinuation, or (ii) reinitiation of NIV within 48 h of NIV discontinuation. Decision for re-intubation and reinitiation of NIV was made using a standard protocol (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).14 NIV was reinitiated using the same setting that the subject received prior to weaning for the subsequent 24 h. The secondary outcomes were the duration of NIV and mechanical ventilation (both noninvasive and invasive), time to intubation, weaning failure (discharge on home NIV), physician’s ease of use of the NIV mode on visual analog scale (on a scale of 100 mm, with 0 being very easy and 100 being very difficult), subject’s visual analog scale for comfort (0 being very comfortable and 100 being very uncomfortable) while on NIV, asynchrony index, severe asynchrony (ie, asynchrony index > 10%), trends of clinical and blood gas parameters, complications related to NIV, length of ICU and hospital stay, hospital mortality, and 90-d mortality.
Statistical Analysis
Results are presented in a descriptive fashion as mean ± SD, median and interquartile range (IQR), or number and percentage. The differences between means of continuous and categorical variables were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test (or Student t test) and chi-square tests, respectively. The trends in vital signs (breathing frequency and mean arterial blood pressure), arterial blood gas values (pH,  ,
,  ), and NIV parameters (peak inspiratory pressure, PEEP, tidal volume, and asynchrony events) were analyzed using a mixed-model technique (autoregressive method) for repeated-measures analysis of variance; the within-groups factor was time (at baseline, 1, 2, 4, and 24 h), while the between-groups factor was the treatment arm.15 The change in the proportion of subjects with severe asynchrony index over time was assessed using the Cochran Q test. We performed competing risk analysis to compare the duration of NIV, mechanical ventilation, and duration of ICU stay with death as a competing risk. Statistical significance was assumed at a P value < .05. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 23 (IBM, Armonk, New York).
), and NIV parameters (peak inspiratory pressure, PEEP, tidal volume, and asynchrony events) were analyzed using a mixed-model technique (autoregressive method) for repeated-measures analysis of variance; the within-groups factor was time (at baseline, 1, 2, 4, and 24 h), while the between-groups factor was the treatment arm.15 The change in the proportion of subjects with severe asynchrony index over time was assessed using the Cochran Q test. We performed competing risk analysis to compare the duration of NIV, mechanical ventilation, and duration of ICU stay with death as a competing risk. Statistical significance was assumed at a P value < .05. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 23 (IBM, Armonk, New York).
Results
Of the 343 screened patients, 243 were excluded before randomization (Fig. 1). Fifty-five patients (16%) did not meet the inclusion criteria (diagnosis of ARF or eligibility for preemptive NIV as per the study protocol), while an additional 188 patients (54.8%) were excluded because of poor sensorium, lack of consent, and other reasons (Fig. 1). Finally, 100 subjects were randomized to either the NAVA arm (n = 50) or the PSV arm (n = 50).
Flow chart. NAVA = neurally-adjusted ventilatory assist; NIV = noninvasive ventilation; PSV = pressure support ventilation.
The mean ± SD age of the study population (60% male) was 56.7 ± 12.0 y and was similar in both the groups (Table 1). A majority (64%) of the subjects had at least 1 comorbid illness. The most common indication for NIV was acute hypercapnic respiratory failure (69%), followed by acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (17%) and preemptive use of NIV (14%). There was no statistical difference between the 2 groups in the indication for NIV (P = .43). The mean ± SD duration of prior invasive mechanical ventilation in patients receiving preemptive NIV was 1.1 ± 3.1 d and was not different between the 2 groups (P = .28). Other baseline clinical and laboratory parameters were also similar between the groups. The median (IQR) pressure support and NAVA level at NIV initiation were 9.0 (7.0–10.0) cm H2O and 0.6 (0.5–0.8) cm H2O/µV for the PSV and NAVA groups, respectively.
Baseline Characteristics of Subjects at ICU Admission
Primary Outcomes
Overall, NIV failed in 31% of the subjects. We did not detect any difference in the NIV failure rates between the 2 arms (NAVA vs PSV: 30% vs 32%, P = .83) (Table 2). Among the NIV failures, 28 subjects required endotracheal intubation, while 3 subjects required NIV within 48 h of tube removal. The intubation rates were similar between the NAVA and the PSV arms (13 [26%] vs 15 [30%], P = .66). There was also no difference in the 28-d mortality between the 2 groups (NAVA vs PSV, 9 [18%] vs 17 [34%], P = .07).
Primary and Secondary Outcomes
Secondary Outcomes
The median (IQR) time to intubation was similar between the 2 groups (NAVA vs PSV; 4.2 [2.6–9.8] vs 4.5 [3.0–40.5] h, P = .39). The length of ICU stay was significantly less in the NAVA arm (sub hazard ratio [95% CI], 0.9 [0.8–0.9], P = .003) (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). There was no difference in the duration of NIV or the total duration of mechanical ventilation. The visual analog scale score for the physician’s ease of use and the patient’s comfort were also similar in both study arms. The use of NAVA during NIV was associated with a higher survival at 90 d (Table 2). The use of NIV was safe, and only minor complications were encountered. However, complications attributed to NIV use were significantly higher in the PSV arm. Abdominal distention (NAVA vs PSV: 6% vs 20%, P = .04) and facial excoriation (NAVA vs PSV: 14% vs 36%, P = .01) were significantly less common in the NAVA group compared to the PSV group.
There was a significant reduction in breathing frequency, peak pressure, and peak EAdi and significant improvement in pH and  as compared to the baseline in both study arms. The use of NAVA resulted in better muscle unloading as highlighted by the lower peak EAdi values at each measured time point compared to the PSV arm. Further, although the peak pressure at NIV initiation was higher in the NAVA arm than in the PSV arm, it rapidly improved over the initial 24 h in the NAVA arm while it remained same in the PSV arm (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).
as compared to the baseline in both study arms. The use of NAVA resulted in better muscle unloading as highlighted by the lower peak EAdi values at each measured time point compared to the PSV arm. Further, although the peak pressure at NIV initiation was higher in the NAVA arm than in the PSV arm, it rapidly improved over the initial 24 h in the NAVA arm while it remained same in the PSV arm (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).
The asynchrony index (median [IQR]) was significantly lower in the NAVA arm than in the PSV arm (6.7 [0–15.3]/min vs 44.8 [31.0–66.7/min], P < .001). The proportion of subjects with severe asynchrony index (ie, > 10%) was also significantly lower in NAVA arm as compared to PSV arm (38% vs 96%, P < .001). The use of NAVA resulted in significantly fewer premature cycling events and a significantly shorter trigger delay (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).
In the post hoc analysis of subjects with COPD exacerbation, the use of NAVA resulted in significantly lower 28-d mortality (P = .01) (Table 3). There was however, no difference in NIV failure rates, duration of NIV, and length of ICU and hospital stay (Table 3).
Outcomes of Subjects With COPD Exacerbation
Discussion
We found no difference in the NIV failure rates or mortality with the use of NAVA compared to PSV in subjects with ARF. However, the use of NAVA resulted in significantly better patient-ventilator interaction. In a post hoc analysis, the use of NAVA significantly improved survival in subjects with COPD exacerbation.
NIV is widely used as the first-line treatment for patients with ARF, especially hypercapnic ARF. Unfortunately, the failure rates with NIV still remain high (up to 50%), particularly in those with hypoxemic ARF.16-18 One important reason for NIV failure is patient-ventilator asynchrony. In a recent systematic review of small physiological studies,7,13,19-21 we noted that use of NAVA during NIV resulted in significantly lower patient-ventilator asynchrony.7 NAVA was also associated with a significantly lower proportion of subjects with severe asynchrony (ie, > 10%).7 Both of these findings were also observed in the current study, where we identified a significant reduction in both asynchrony index and severe asynchrony index.
Despite better patient-ventilator interaction, the use of NAVA did not improve NIV failure rates or hospital mortality. One obvious reason is the inclusion of a heterogenous population with ARF. NIV failure rates are higher in those with hypoxemic compared to hypercapnic respiratory failure, especially those with ARDS.16,18,22,23 This was also demonstrated in the subgroup analysis of subjects with an exacerbation of COPD, in whom the use of NAVA significantly reduced the 28-d mortality (Table 3). However, NIV failure rates, duration of NIV, and length of hospital stay were not different compared to PSV. A recent study of NAVA in subjects with COPD exacerbation made a similar observation.24
In this study, we noted 2 unexpected results. First, the use of NAVA resulted in a 20% reduction in 90-d mortality. This could be attributed to lower in-hospital mortality in subjects with COPD exacerbation, which might have contributed to better 90-d mortality. The better 90-d survival in the NAVA arm could also be due to unmeasured comorbidities or the severity of the underlying disease, or it could be a chance finding. Second, the use of NAVA resulted in a lower frequency of abdominal distention (6% and 20% in NAVA and PSV arms, respectively) and skin ulcers (14% and 36% in NAVA and PSV arms, respectively). This could have been due to the better synchrony of the patient’s inspiration with the ventilator-delivered breath, resulting in less aerophagia and lower frequency of mask displacement.
What are the clinical implications of this study? Our findings indicate that NIV can be safely delivered using NAVA for a prolonged duration. Further, NAVA can be used during NIV to manage subjects presenting with ARF of different etiologies. The use of NAVA results in better diaphragmatic unloading, as indicated by a more marked reduction in peak EAdi.25 Thus, this study provides the basis for future research into clinical outcomes using NAVA during NIV, particularly for patients with COPD exacerbation. The NIV failure rate was 52% in the PSV arm and 37% in the NAVA arm (power 0.8, alpha 0.05). Keeping NIV failure as the primary outcome, 186 subjects would be required in each arm. The 28-d mortality was 34% in the PSV arm and 18% in the NAVA arm. Using this information from the current study, 130 subjects would be required in each arm.
Finally, our study has a few limitations. This was a single-center study with a small sample size. We also included a heterogeneous population of subjects. However, the study population reflects the typical scenario in any respiratory ICU, thereby representing a real-world situation. Due to limitations of the ventilator software, we recorded the high-resolution waveform for only 20 s at a time. We obtained 3 readings (each for 20 s, at 5-min intervals) to present data for 1 min. This might reduce the confidence in our measurements. The strength of the study is the use of objective criteria for intubation and the use of NAVA catheters in both groups to assess patient-ventilator interaction. Another important strength of our study is that we did not use sedation, thereby avoiding the effects of sedation on the ventilatory modes compared.
Conclusions
The use of NAVA during NIV did not improve NIV failure rates or 28-d mortality in subjects with ARF. However, use of NAVA reduced the frequency or severity of patient-ventilator asynchrony and NIV-related complications. The finding of improved survival in subjects with COPD exacerbation with NAVA requires further evaluation in a larger trial.
Footnotes
- Correspondence: Inderpaul Singh Sehgal MD DM, Assistant Professor, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh 160012, India. E-mail: inderpgi{at}outlook.com
Drs Prasad and Gandra are co-first authors.
Supplementary material related to this paper is available at http://www.rcjournal.com.
The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
- Copyright © 2021 by Daedalus Enterprises








