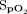Abstract
BACKGROUND: Pulse oximeters are used to measure 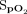 and pulse rate. These devices are either standalone machines or integrated into physiologic monitoring systems. Some smartphones now have pulse oximetry capabilities. Because it is possible that some patients might utilize this technology, we sought to assess the accuracy and usability of smartphone pulse oximeters.
and pulse rate. These devices are either standalone machines or integrated into physiologic monitoring systems. Some smartphones now have pulse oximetry capabilities. Because it is possible that some patients might utilize this technology, we sought to assess the accuracy and usability of smartphone pulse oximeters.
METHODS: This was a prospective, observational study that involved noninvasive measurements of  and heart rate with 3 devices: Masimo Radical-7, Kenek Edge with the Apple iPhone 6S, and the Samsung S8 smartphone. Ambulatory adult patients visiting our institution’s pulmonary function lab for a 6-min walk test were eligible to participate in the study. Pretest and posttest results for each subject were obtained simultaneously using all 3 devices. All results were analyzed with the Spearman rho correlation test, and Bland-Altman plots were used to assess the agreement of measures between the devices.
and heart rate with 3 devices: Masimo Radical-7, Kenek Edge with the Apple iPhone 6S, and the Samsung S8 smartphone. Ambulatory adult patients visiting our institution’s pulmonary function lab for a 6-min walk test were eligible to participate in the study. Pretest and posttest results for each subject were obtained simultaneously using all 3 devices. All results were analyzed with the Spearman rho correlation test, and Bland-Altman plots were used to assess the agreement of measures between the devices.
RESULTS: Forty-seven subjects were enrolled in the study, with pulmonary hypertension (30%) and COPD (23%) being the 2 major diagnoses. The mean ± SD difference between the Masimo and Apple devices for pretest  was 2.3 ± 2.4%, and the difference for posttest
was 2.3 ± 2.4%, and the difference for posttest 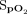 was 2.1 ± 3.9%. The mean difference between the Masimo and Samsung devices for pretest
was 2.1 ± 3.9%. The mean difference between the Masimo and Samsung devices for pretest 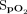 was 3.2 ± 2.8%, and the difference for posttest
was 3.2 ± 2.8%, and the difference for posttest 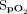 was 2.4 ± 3.5%. The number of subjects who were unable to obtain
was 2.4 ± 3.5%. The number of subjects who were unable to obtain 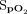 was higher with the Samsung device than with the Apple device in both pretest (14 of 47 vs 3 of 47) and posttest (17 of 47 vs 5 of 47). In contrast, the Masimo device was able to measure
was higher with the Samsung device than with the Apple device in both pretest (14 of 47 vs 3 of 47) and posttest (17 of 47 vs 5 of 47). In contrast, the Masimo device was able to measure  in all subjects.
in all subjects.
CONCLUSIONS: Smartphone pulse oximeters were unreliable compared to a hospital pulse oximeter. Further research is needed with evolving technology to better understand smartphone pulse oximetry. (ClinicalTrials.gov registration NCT03534271.)
Introduction
Pulse oximeters are commonly used medical devices that are utilized for monitoring  and measuring heart rate. Clinicians use these devices in a hospital or clinical setting to monitor the effects of oxygen therapy or to detect the presence of hypoxemia in a quick and noninvasive manner. Pulse oximeters are either standalone devices or integrated into complex physiologic monitoring systems.1 While frequently utilized by medical professionals, pulse oximeters are also available to the general public for use as a monitoring device, particularly for patients with COPD, asthma, pulmonary hypertension, and other respiratory conditions.2 Non-medically trained individuals may use this technology as a monitoring tool for conditions such as dyspnea, sleep apnea, or cardiac arrythmias.3 While home pulse oximetry is potentially useful, a potential barrier to its use is expense, especially for those with limited resources.4
and measuring heart rate. Clinicians use these devices in a hospital or clinical setting to monitor the effects of oxygen therapy or to detect the presence of hypoxemia in a quick and noninvasive manner. Pulse oximeters are either standalone devices or integrated into complex physiologic monitoring systems.1 While frequently utilized by medical professionals, pulse oximeters are also available to the general public for use as a monitoring device, particularly for patients with COPD, asthma, pulmonary hypertension, and other respiratory conditions.2 Non-medically trained individuals may use this technology as a monitoring tool for conditions such as dyspnea, sleep apnea, or cardiac arrythmias.3 While home pulse oximetry is potentially useful, a potential barrier to its use is expense, especially for those with limited resources.4
Recently, camera-based pulse oximetry applications (apps) have been embedded in smartphones to enable individuals to monitor 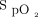 and heart rate from their personal devices. In addition, portable, external pulse oximeters that are compatible with smartphones have been produced. This provides additional access to pulse oximetry for many individuals, as smartphones are common in many industrialized countries.4 Some studies have shown this technology to be promising, and in cases involving healthy subjects, it was found to be noninferior to standard pulse oximetry devices.2-7 Tomlinson et al2 evaluated the accuracy of 2 different smartphone-based pulse oximetry apps (probe-based and camera-based) in healthy pediatric subjects. They reported that probe-based apps were more reliable and precise than camera-based apps. They pointed out that future studies should be conducted in hypoxemic patients to assess the accuracy with desaturations.2
and heart rate from their personal devices. In addition, portable, external pulse oximeters that are compatible with smartphones have been produced. This provides additional access to pulse oximetry for many individuals, as smartphones are common in many industrialized countries.4 Some studies have shown this technology to be promising, and in cases involving healthy subjects, it was found to be noninferior to standard pulse oximetry devices.2-7 Tomlinson et al2 evaluated the accuracy of 2 different smartphone-based pulse oximetry apps (probe-based and camera-based) in healthy pediatric subjects. They reported that probe-based apps were more reliable and precise than camera-based apps. They pointed out that future studies should be conducted in hypoxemic patients to assess the accuracy with desaturations.2
Currently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration does not regulate smartphone-integrated health-related apps, and the accuracy of pulse oximetry apps in hypoxemic patients is unknown.2 This is concerning because device inaccuracies could provide false information that may lead to an improper or unnecessary reaction. Smartphone manufacturers include disclaimers specifically stating that the applications are not intended for use in disease diagnosis or are not intended for use as medical devices. However, because it is possible that some individuals could utilize this technology for home use or remotely, we sought to assess smartphone pulse oximeters in subjects at risk for hypoxemia. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the reliability and usability 2 smartphone pulse oximeters in adult subjects undergoing a 6-min walk test (6MWT), with comparisons made to a standard pulse oximeter used in a pulmonary function laboratory.
Quick Look
Current Knowledge
Pulse oximeters are noninvasive medical devices that monitor 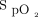 and pulse rate. Current evidence suggests that smartphone pulse oximetry may be accurate in healthy individuals. The reliability of these devices in patients at risk for hypoxemia is not known.
and pulse rate. Current evidence suggests that smartphone pulse oximetry may be accurate in healthy individuals. The reliability of these devices in patients at risk for hypoxemia is not known.
What This Paper Contributes to Our Knowledge
In subjects at risk for hypoxemia, smartphone pulse oximetry technology was unreliable when compared to a medical pulse oximeter. Smartphone pulse oximeters were unable to consistently detect and display measured pulse rate and 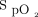 values. They also measured
values. They also measured 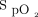 consistently lower than the hospital pulse oximeter. Smartphone pulse oximetry devices cannot be recommended as a replacement for medical oximeters.
consistently lower than the hospital pulse oximeter. Smartphone pulse oximetry devices cannot be recommended as a replacement for medical oximeters.
Methods
This study was a single-center observational study conducted in an out-patient pulmonary function test laboratory at Rush University Medical Center, a large urban academic medical center in Chicago, Illinois. The study was approved by the institutional review board. Consent was waived as the study involved minimal risks to the subjects and the information obtained from the mobile devices was not used to make clinical decisions.
Adult subjects who were ambulatory and scheduled to perform a 6-min walk test in the pulmonary function test lab were included. Patients were excluded from the study if any of the following criteria were met: (1) unable to perform the study due to institutional standards, such as blood pressure > 180/90 mm Hg or < 70/50 mm Hg; were light-headed, dizzy, experienced syncope, or had severe headaches; 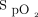 was ≤ 85% on supplemental oxygen; or if patients were on oxygen > 4 L/min; (2) patient had a known gait issue that may result in a fall, or patient required the use of a walker but did not bring it. Demographic information, including age, race, gender, and weight, were collected. If the test was terminated, all measurements were recorded at the time of termination and the reason for termination was recorded.
was ≤ 85% on supplemental oxygen; or if patients were on oxygen > 4 L/min; (2) patient had a known gait issue that may result in a fall, or patient required the use of a walker but did not bring it. Demographic information, including age, race, gender, and weight, were collected. If the test was terminated, all measurements were recorded at the time of termination and the reason for termination was recorded.
Pulse rate and 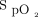 were measured using an Apple iPhone 6S (Apple, Cupertino, California) with an attached external finger probe pulse oximeter (Kenek Edge, LionsGate Technologies, Vancouver, Canada) (Fig. 1), a Samsung S8 (Samsung Electronics, Seoul, South Korea) with a built-in pulse oximeter (Fig. 2), and a Masimo pulse oximeter with a forehead probe (Masimo, Irvine, California). The Samsung pulse oximetry app is a built-in app (Samsung Health) with no additional cost. The Kenek Edge used with the Apple iPhone is an external device purchased from the stated manufacturer; the cost of device is approximately $39.95. Measurements for smartphone pulse oximeters were collected immediately before and after 6MWT using the same finger or arm when possible. Measurements were collected with all 3 devices simultaneously. Pretest and posttest results were obtained for each subject. When devices failed to provide a heart rate or
were measured using an Apple iPhone 6S (Apple, Cupertino, California) with an attached external finger probe pulse oximeter (Kenek Edge, LionsGate Technologies, Vancouver, Canada) (Fig. 1), a Samsung S8 (Samsung Electronics, Seoul, South Korea) with a built-in pulse oximeter (Fig. 2), and a Masimo pulse oximeter with a forehead probe (Masimo, Irvine, California). The Samsung pulse oximetry app is a built-in app (Samsung Health) with no additional cost. The Kenek Edge used with the Apple iPhone is an external device purchased from the stated manufacturer; the cost of device is approximately $39.95. Measurements for smartphone pulse oximeters were collected immediately before and after 6MWT using the same finger or arm when possible. Measurements were collected with all 3 devices simultaneously. Pretest and posttest results were obtained for each subject. When devices failed to provide a heart rate or  value, it was recorded as “unable to obtain.”
value, it was recorded as “unable to obtain.”
Kenek Edge with Apple iPhone 6S.
Samsung S8.
Standard disinfection policies were applied, personal protective equipment was worn according to institution guidelines, and the approved protocol was followed at all times. Subject safety and privacy was addressed throughout the study.
Statistical Analysis
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic test was used to test the normality of distribution for considered variables. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SD or median (interquartile range), depending on the normality of distribution. Before and after variables in each device were compared with a paired t test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The Spearman rho correlation coefficient was used to measure the relationship between devices. Bland-Altman plots were used to compare the agreement in 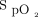 measurements between the different devices.8 The upper and lower limits of agreement were set at ± 1.96 SD of the mean difference, as is the norm for Bland-Altman plots, signifying the 95% CI. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Data analysis was conducted with SPSS 23.0 (SPSS; Chicago, Illinois).
measurements between the different devices.8 The upper and lower limits of agreement were set at ± 1.96 SD of the mean difference, as is the norm for Bland-Altman plots, signifying the 95% CI. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Data analysis was conducted with SPSS 23.0 (SPSS; Chicago, Illinois).
Results
During the study period, 47 subjects were enrolled, and they completed the study with no adverse events. The Masimo device was able to record pretest and posttest heart rate and 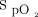 on all 47 subjects.
on all 47 subjects.
Subjects’ Demographic Information
Among the 47 subjects (11 male), 26 (55%) were African-American and 13 (28%) were white. The major diagnoses in the subjects were pulmonary hypertension (30%) and COPD (23%) (Table 1). Other diagnoses included asthma (4%), congestive heart failure (9%), pulmonary fibrosis (6%), and renal disease (9%). Fourteen subjects (30%) used oxygen at home, and 4 subjects terminated the 6MWT early. The median age was 69 y (IQR 57–76).
Subject Demographics
Ability to Measure Heart Rate and 
The Apple device was able to record the pretest and posttest parameters of heart rate and  in 44 and 42 subjects, respectively. The Samsung device was able to record pretest and posttest parameters of heart rate and
in 44 and 42 subjects, respectively. The Samsung device was able to record pretest and posttest parameters of heart rate and 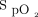 in 33 and 30 subjects, respectively (Table 2). The number of subjects who were unable to obtain
in 33 and 30 subjects, respectively (Table 2). The number of subjects who were unable to obtain 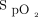 measures was higher with the Samsung device than with the Apple device in both pretest (14 of 47 vs 3 of 47) and posttest (17 of 47 vs 5 of 47) measurements.
measures was higher with the Samsung device than with the Apple device in both pretest (14 of 47 vs 3 of 47) and posttest (17 of 47 vs 5 of 47) measurements.
Summary of Calculated Values for 3 Devices
Pulse Rate Measurements
For the pre-6MWT pulse rate measurements, there was a strong positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Apple device (n = 44, r = 0.98, P < .001). There was a strong positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Samsung device (n = 33, r = 0.98, P < .001).
For the post-6MWT pulse rate measurements, there was a strong positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Apple device (n = 42, r = 0.92, P < .001). There was also a strong positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Samsung device (n = 30, r = 0.890, P < .001).
 Measurements
Measurements
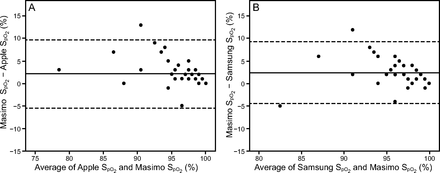
For the pre-6MWT 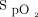 measurements, there was a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Apple device (n = 44, r = 0.72, P < .001). There was also a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Samsung device (n = 33, r = 0.62, P < .001).
measurements, there was a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Apple device (n = 44, r = 0.72, P < .001). There was also a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Samsung device (n = 33, r = 0.62, P < .001).
For the post-6MWT 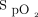 measurements, there was a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Apple device (n = 42, r = 0.66, P < .001). There was a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and Samsung device (n = 30, r = 0.67, P < .001).
measurements, there was a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and the Apple device (n = 42, r = 0.66, P < .001). There was a moderate positive correlation between the Masimo device and Samsung device (n = 30, r = 0.67, P < .001).
Bland-Altman Analysis
Bland-Altman plots were used to demonstrate the agreement between the Masimo device  measurements and the Apple device
measurements and the Apple device 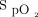 measurements before the 6MWT (Figure 3A). The mean difference or bias between the devices was 2.3 ± 2.4%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –2.4% to 7.0%. The mean difference or bias between the pre-6MWT Masimo device
measurements before the 6MWT (Figure 3A). The mean difference or bias between the devices was 2.3 ± 2.4%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –2.4% to 7.0%. The mean difference or bias between the pre-6MWT Masimo device 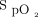 measurements and the Samsung device
measurements and the Samsung device 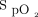 measurements (Figure 3B) was 3.2 ± 2.8%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –2.3% to 8.7%. The Masimo device measures
measurements (Figure 3B) was 3.2 ± 2.8%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –2.3% to 8.7%. The Masimo device measures 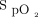 consistently higher than both the Apple and Samsung devices.
consistently higher than both the Apple and Samsung devices.
Bland-Altman plots for pre-test  for Apple and Samsung devices, respectively. Solid lines show the mean bias. Dashed lines represent upper and lower limits of agreement at ± 1.96 SD.
for Apple and Samsung devices, respectively. Solid lines show the mean bias. Dashed lines represent upper and lower limits of agreement at ± 1.96 SD.
Bland-Altman plots were also used to demonstrate the agreement between the Masimo device  measurements and the Apple device
measurements and the Apple device 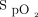 measurements after the 6MWT (Figure 4A). The mean difference or bias between the devices was 2.1 ± 3.9%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –5.5% to 9.7%. The mean difference or bias between the post-6MWT Masimo device
measurements after the 6MWT (Figure 4A). The mean difference or bias between the devices was 2.1 ± 3.9%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –5.5% to 9.7%. The mean difference or bias between the post-6MWT Masimo device  measurements and the Samsung device
measurements and the Samsung device 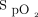 measurements (Figure 4B) was 2.4 ± 3.5%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –4.5% to 9.3%. The Masimo device consistently measured
measurements (Figure 4B) was 2.4 ± 3.5%, and the limits of agreement ranged from –4.5% to 9.3%. The Masimo device consistently measured 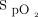 higher than both the Apple and Samsung devices.
higher than both the Apple and Samsung devices.
Bland-Altman plots for post-test  for Apple and Samsung devices, respectively. Solid lines show the mean bias. Dashed lines represent upper and lower limits of agreement at ± 1.96 SD.
for Apple and Samsung devices, respectively. Solid lines show the mean bias. Dashed lines represent upper and lower limits of agreement at ± 1.96 SD.
Discussion
There is a wide variety of smartphones available that have the capability to manage and track personal medical information through apps. Smartphone pulse oximetry apps make it simple for individuals to monitor their heart rate and 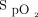 at home or remotely. Many individuals who utilize home oxygen or who have chronic lung disease may find it useful and convenient to manage their daily activities by monitoring
at home or remotely. Many individuals who utilize home oxygen or who have chronic lung disease may find it useful and convenient to manage their daily activities by monitoring  and heart rate through smartphone pulse oximeters. Thus, this study was necessary to determine whether data obtained from smartphone apps can be useful.
and heart rate through smartphone pulse oximeters. Thus, this study was necessary to determine whether data obtained from smartphone apps can be useful.
To our knowledge, this is the first study to assess smartphone pulse oximetry technology in subjects at risk for hypoxemia in a pulmonary function lab. Tomlinson et al2 assessed healthy pediatric subjects using smartphone apps, and Alexander et al7 studied healthy adult populations. Both studies reported that smartphone pulse oximeters were accurate, although the accuracy in hypoxemic subjects remained unknown.
In a more recent study, Tayfur and Afacan3 sought to evaluate the accuracy of smartphone measurements of  and heart rate compared to an arterial blood gas analysis machine (for
and heart rate compared to an arterial blood gas analysis machine (for  ) and a vital sign monitor (for heart rate) in an emergency department setting. Similar to our study, they used the Samsung S8 smartphone device. They analyzed data from 101 subjects in various disease groups, with approximately 42% of their subjects included in the pulmonary disease group. They concluded that the smartphone values were consistent with the reference devices.3 The authors noted that advances in technology may be improving smartphone pulse oximetry.
) and a vital sign monitor (for heart rate) in an emergency department setting. Similar to our study, they used the Samsung S8 smartphone device. They analyzed data from 101 subjects in various disease groups, with approximately 42% of their subjects included in the pulmonary disease group. They concluded that the smartphone values were consistent with the reference devices.3 The authors noted that advances in technology may be improving smartphone pulse oximetry.
Smartphone manufacturers include disclaimers that specifically state that the apps are not intended for use in disease diagnosis (https://www.samsung.com/us/samsung-health. Accessed January 3, 2020), or are not for use as medical devices, intended only for sports, aviation, and recreational uses (https://lgtmedical.com/kenek/edge.html. Accessed January 3, 2020). Despite the disclaimers, individuals may still opt to use the technology to monitor their heart rate and  . The results of our study support the disclaimers of the smartphone manufacturers, namely that smartphone pulse oximetry should not be used for medical purposes. Our study showed that measurements were completely undetected by smartphones (documented as “unable to obtain”) in some subjects, but these measurements were obtained with the Masimo device pulse oximeter. In some individuals, the smartphone devices took longer to display values compared to the Masimo device. Interestingly, heart rate values obtained from both devices correlated strongly with the Masimo device. We acknowledge that the devices do read
. The results of our study support the disclaimers of the smartphone manufacturers, namely that smartphone pulse oximetry should not be used for medical purposes. Our study showed that measurements were completely undetected by smartphones (documented as “unable to obtain”) in some subjects, but these measurements were obtained with the Masimo device pulse oximeter. In some individuals, the smartphone devices took longer to display values compared to the Masimo device. Interestingly, heart rate values obtained from both devices correlated strongly with the Masimo device. We acknowledge that the devices do read  accurately in some subjects. However due to the inconsistency of results, specifically the “unable to obtain” values, and because the smartphone devices read consistently lower than the Masimo device both before and after the 6MWT, we cannot recommend these devices for use in patients at risk for hypoxemia.
accurately in some subjects. However due to the inconsistency of results, specifically the “unable to obtain” values, and because the smartphone devices read consistently lower than the Masimo device both before and after the 6MWT, we cannot recommend these devices for use in patients at risk for hypoxemia.
Pulse oximeters have known limitations due to low perfusion, skin pigmentation, intravenous dyes, motion artifacts, nail polish, and dyshemoglobins.1,9 At this time, it is uncertain what factors, if any, affect the reliability of smartphone pulse oximetry. Further research is suggested for patients with lung or cardiac disease who may have conditions affecting blood flow to the fingers to assess whether skin deformities impact reliability of smartphone pulse oximetry technology.
There are several limitations to this study. First, this was a single-center study with only 47 subjects. The sample size limitation prohibits an evaluation of how smartphone pulse oximetry functions in various disease states. Second, the time between measured parameters was inconsistent. While values were collected simultaneously, the 3 devices displayed results at different times. We noticed during the study that the camera-based technology had a longer read time before results were displayed. We are unsure what impact, if any, that had on our results. We were unable to use the same hand due to the bulkiness of the finger probes and smartphone devices. The forehead probe was used as a standard (control) model, and upper extremities were used as the study measure. Finally,  was not used in our study because arterial blood gas samples were not drawn immediately before or after the 6MWT. Calculating the root mean square of the differences between the measured and actual values is the reporting standard used by the Food and Drug Administration. This variable reflects the accuracy of pulse oximetry devices, but it requires arterial blood oximetry.10 As more of the population relies on smartphones for medical monitoring, future investigation that determines device accuracy based on clinical standards is essential.
was not used in our study because arterial blood gas samples were not drawn immediately before or after the 6MWT. Calculating the root mean square of the differences between the measured and actual values is the reporting standard used by the Food and Drug Administration. This variable reflects the accuracy of pulse oximetry devices, but it requires arterial blood oximetry.10 As more of the population relies on smartphones for medical monitoring, future investigation that determines device accuracy based on clinical standards is essential.
Conclusions
The results of our study indicate that smartphone pulse oximeters are not a reliable way to obtain heart rate and  measurements in patients who are at risk for hypoxemia. We agree with the manufacturers that these devices should not be used as medical devices at this time. External probe-based technology was found to be more reliable than camera-based technology, but this finding warrants more investigation. Further studies evaluating smartphone pulse oximeters compared to hospital-grade finger-probe oximeters and compared to blood oximetry are recommended. Also, as smartphone technology continues to improve, studies to assess accuracy and reliability in various disease states are warranted.
measurements in patients who are at risk for hypoxemia. We agree with the manufacturers that these devices should not be used as medical devices at this time. External probe-based technology was found to be more reliable than camera-based technology, but this finding warrants more investigation. Further studies evaluating smartphone pulse oximeters compared to hospital-grade finger-probe oximeters and compared to blood oximetry are recommended. Also, as smartphone technology continues to improve, studies to assess accuracy and reliability in various disease states are warranted.
Acknowledgement
We thank Sharon Foley PhD RDN, for assistance with statistical analysis.
Footnotes
- Correspondence: J Brady Scott MSc RRT RRT-ACCS AE-C FAARC, Rush University, Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences, Division of Respiratory Care, Armour Academic Center, 600 S Paulina St, Suite 751, Chicago, IL 60607. E-mail: jonathan_b_scott{at}rush.edu
Mr Scott presented a version of this paper as an Editors’ Choice abstract at AARC Congress 2019, held November 9–12, 2019, in New Orleans, Louisiana.
Mr Scott discloses relationships with Ventec Life Systems and Teleflex. Dr Li discloses a relationship with Fisher & Paykel. Ms Modi and Ms Kiourkas have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
- Copyright © 2021 by Daedalus Enterprises