Abstract
BACKGROUND: Although studies have confirmed the safety and feasibility of early active mobilization, its implementation status is still unsatisfactory. The most important obstacle is ensuring patient safety. Comprehensively assessing the physical condition of patients considered for mobilization is the basis of safety. However, appropriate guidance is lacking. We performed a systematic review to extract and summarize current safety assessment criteria for the early active mobilization of mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU.
METHODS: A systematic literature search was conducted using English and Chinese databases according to the PRISMA checklist and guidelines to identify relevant original studies that evaluated safety assessment variables and specific parameters.
RESULTS: A total of 24 medium- and high-quality articles involving a total of 4,842 subjects were included in the analysis. Among these studies, there were 15 randomized controlled trials involving 1,777 subjects (888 in the control groups, 889 in the interventional groups) and 9 cohort studies involving 3,065 subjects (1,240 in the control groups, 1,825 in the exposure groups). There were 5 safety assessment criteria, including cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, musculoskeletal, and other. Within these were 17 different variables and 48 specific parameters.
CONCLUSIONS: The safety assessment criteria should focus on cardiac reserve, respiratory reserve, consciousness, and muscle strength. It is especially important to note whether the parameters are stable because parameter stability can be more representative of a patient’s condition than absolute values. We provide a flow diagram for clinical safety assessments; however, some limitations exist, and this assessment requires further validation and optimization.
Introduction
The reported incidence of ICU-acquired weakness among critically ill patients in the ICU is 25–50%.1,2 ICU-acquired weakness is associated with substantial impairment in physical functioning and a poor 2-y survival rate in critically ill patients.1 It may be aggravated by long-term bed rest due to routine sedation and immobility.3 Currently, early mobilization is a therapeutic intervention used to prevent or attenuate physical functional impairment or ICU-acquired weakness4,5; however, intensive in-bed activities are not sufficient to counteract the adverse effects of bed rest and immobility, so patients are encouraged to perform active out-of-bed activities.6 The implementation of active out-of-bed activities is still poor, however, mainly due to concerns regarding patient safety.7 Some studies have proposed safety assessment criteria for early mobilization, but unified assessment guidelines have not been established. Only one formal set of safety criteria based on expert consensus has been proposed for active mobilization safety assessment.8 In reviewing the literature, we found that some studies refer to expert consensus on when to implement active mobilization, but, in general, safety assessment protocols are not uniform. For inexperienced ICU medical staff, this situation is not conducive to the implementation of active mobilization while ensuring patient safety. In China, related guidance is currently lacking. However, due to disparities in professional experience and equipment, expert consensus is not fully suitable for China’s national conditions. This systematic review aims to compile safety assessment criteria for early active mobilization and to provide a basis for the development of safety assessment guidance for mechanically ventilated ICU patients in China.
Methods
Search Strategy
This systematic review followed the PRISMA checklist and guidelines. We searched 9 databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Ovid, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, China Biology Medicine, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chongqing VIP, and WanFang Data, from their inception until December 31, 2019. The following key terms were used: (“mechanical ventilation,” “intubated,” “artificial respiration”) and (“early rehabilitation,” “early mobilization,” “early ambulation,” “early mobility,” “early activity,” “early action,” “early motion,” “early exercise,” “early movement,” “active mobilization,” “exercise rehabilitation,” “mobility intervention,” “exercise intervention,” “accelerated ambulation,” “rehabilitation exercise,” “exercise therapy,” “out-of-bed,” and “motor activity”). Furthermore, a manual search of the references of all included articles and previous review articles was performed to identify additional studies. The protocol of this review was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42020163685). An example of the search strategy using PubMed is shown in the online supplement (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). This research received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
To comprehensively compile current safety assessment criteria, there was no restriction on the study type during the literature search process. However, only original studies were finally included. All subjects were > 18 y old, admitted to the ICU, and treated with mechanical ventilation for > 24 h. In the randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the control group received the usual ICU care, while the intervention group underwent early mobilization, including active mobilization which we categorized as in-bed activities or out-of-bed activities (Table 1). In the cohort studies, the exposure group underwent early mobilization, including active mobilization. Articles in English and Chinese were included. The methods sections of the articles included descriptions of the safety assessment variables and specific parameters used to initiate early active mobilization. Articles in which only active in-bed activities and no out-of-bed activities were reported were excluded, as were duplicate publications.
Basic Characteristics of Included Studies
Study Selection and Methodological Quality
A literature screening and methodological quality assessment were performed independently by 2 researchers. First, titles and abstracts of the articles were screened, and then the full texts were screened while considering the eligibility criteria. The RCTs were assessed according to the Cochrane 5.1.0 manual.9 If all risk of bias criteria were met, the study was unlikely to be biased and rated as Grade A; if the criteria were partially met, then the possibility of bias was moderate and the study was rated as Grade B; if the criteria were not met, the study was likely to be biased and rated as Grade C.10 Cohort studies were evaluated with the Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale, and scores of 6–9 were considered good.11 Disagreement between the 2 researchers was resolved by discussion or by consultation with a third researcher.
Data Extraction and Variable Selection
The data were extracted from the eligible studies and recorded on a standardized data collection form by two researchers independently; the data included the basic characteristics of the studies and the safety assessment criteria. The safety assessment criteria were categorized as cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, musculoskeletal and other, and involved related variables and specific parameters.
Results
Search Results
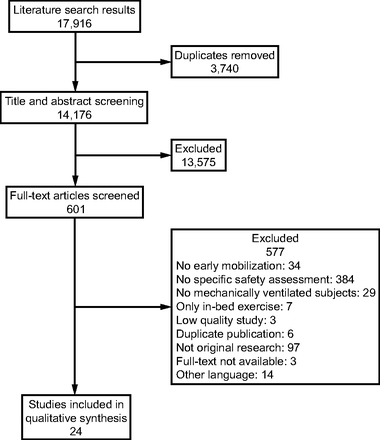
In total, 17,916 records were initially identified; of these records, 7,957 studies were found in Chinese databases, 9,956 studies were found in English databases, and 3 studies were identified by other search methods. After removing duplicates, 14,176 records remained. After reading the titles and abstracts, 13,575 records that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded, and the full texts of the remaining articles were further evaluated. Finally, 24 articles were included (see Fig. 1).
Flow chart.
Study Characteristics
In total, 4,842 adult subjects on mechanical ventilation in the general ICU, trauma and burn ICU, cardiothoracic ICU, medical ICU, surgical ICU, respiratory ICU, and neurosciences ICU were included. There were 15 RCTs involving 1,777 subjects (888 in the control groups and 889 in the interventional groups) and 9 cohort studies involving 3,065 subjects (1,240 in the control groups and 1,825 in the exposure groups). In the RCTs, the control groups received the usual ICU care, and the intervention groups received early mobilization in addition to usual ICU care. In the cohort studies, the exposure groups received early mobilization, and the control groups received usual ICU care or there was no control group. Specific active mobilization programs were customized according to the subjects’ condition and mainly involved in-bed activities and out-of-bed activities (Table 1). Adverse events included decreased muscle strength, unplanned extubation, changes in blood pressure, decreased blood oxygen saturation, increased heart rate, decreased blood glucose level, restlessness, and instability to stand. The incidence of adverse events was < 3% (Table 1).
According to the quality assessments, the overall quality was moderate to high. Among the included RCTs, 3 studies (20%) were considered Grade A, and 12 studies (80%) were considered Grade B. Regarding the quality of the included cohort studies, 6 studies (67%) received a 6, 2 studies (22%) received a 7, and 1 study (11%) received a 9. The quality assessment results of the 24 articles are shown in the online supplement (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com).
Safety Assessment Criteria
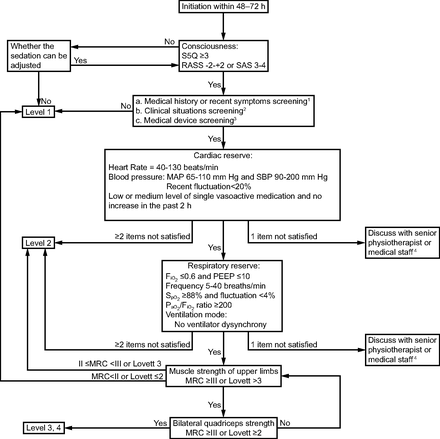
The safety assessment criteria included cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, musculoskeletal, and other criteria and included a total of 17 variables and 48 parameters. Specifically, the cardiovascular criteria included 5 variables (29%) involving 14 parameters, the respiratory criteria included 5 variables (29%) involving 8 parameters, the neurological criteria included 2 variables (12%) involving 7 parameters, the musculoskeletal criteria included 3 variables (18%) involving 7 parameters, and the other criteria included 2 variables (12%) involving 12 parameters (see the supplementary materials at http://www.rcjournal.com). According to the results, a safety assessment flow diagram was constructed (Fig. 2). The flow diagram shows the key assessment variables of 5 criteria, including consciousness, cardiac reserve, respiratory reserve, and muscle strength. Based on the assessment results and the patient’s condition, the appropriate mobilization protocol is recommended.
Mobilization protocol based on safety assessment criteria of the patient’s condition and tolerance. Level 1: Passive or active assisted range of motion exercises in bed, in a semi-Fowler position (30–45°). Level 2: Active assisted or active exercises in bed, in a standard Fowler position (45–60°) to sitting position; exercises performed against gravity or counter-resistance; sitting on the edge of the bed with legs dangling. Level 3/4: Transferring to a chair from the bed, sitting, standing and walking. Notes: (1) No significant cardiac tamponade, acute or unstable angina, acute myocarditis, recent myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, or arrhythmia on electrocardiography; cardiac index ≥ 2.0 L/min/m2; no COPD, asthma, or restrictive lung disease. (2) No unstable fracture, spinal cord injury, deep vein thrombosis, or active bleeding; no body temperature ≥ 38°C, hemoglobin ≤ 70 g/L, platelets ≤ 8 × 109/L, or blood sugar < 6.2 or > 20 mmol/L; intracranial pressure not elevated. (3) Stability of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or continuous renal replacement therapy flows and cannulation position (for patients with femoral cannulation, flexing the hip to 90° prior to mobilization). (4) Consideration of potential risk and consequences of adverse events; if the next step assessment is conducted, authorization should be given by the senior physiotherapist or medical staff. S5Q = standardized 5 questions for cooperation; RASS = Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale; SAS = Sedation-Agitation Scale; MAP = mean arterial pressure; SBP = systolic blood pressure; MRC = Medical Research Council.
Discussion
Compared with previous studies,12,13 this systematic review recommends a more detailed flow diagram for considering safety assessment criteria (Fig. 2). However, the assessment variables and parameters of the safety criteria were obtained only from the assessment methods reported by the researchers included in the analysis, and research specifically supporting the safety of the assessment variables and parameters is lacking. Therefore, our purpose is to provide only a reference for clinical practice rather than a mandatory process. As a recommendation, the assessment should be initiated within 48–72 h after the patient is admitted to the ICU, and the patient needs to be reassessed before each mobilization.14 Through the assessment of the key safety variables and parameters of the cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, musculoskeletal, and other criteria combined with the actual condition and activity tolerance of the patient, a personalized active mobilization protocol can be developed.
Cardiovascular Criteria
Consistent with previous studies, there are many variables and parameters associated with the cardiovascular criteria.12,13 Patients in the ICU experience long-term immobilization. The cardiovascular system needs to perform additional work to maintain cardiac output and cerebral blood supply during the progression of a change in body position during mobilization, potentially resulting in an insufficient cardiac reserve.15 This may not be conducive to patient safety. Heart rate and blood pressure are important in evaluating cardiac reserve, which can be used to judge whether a patient can tolerate mobilization.16 Stiller and Phillips17 reported that the resting heart rate should be < 50% of the target heart rate (220 – age); if this heart rate cannot be achieved, the patient may not have sufficient cardiac reserve. In this regard, the expert consensus proposed that patients with a stable underlying rhythm or any tachyarrhythmia with a ventricular rate < 120 beats/min could receive active mobilization, but medical staff should be cautious while mobilizing those with a rate of 120–150 beats/min.8 This systematic review found that researchers prefer to use 40–130 beats/min as a reference for heart rate assessment and emphasize that the heart rate fluctuation range does not exceed 50%. The heart rate alone cannot indicate the safety of the active mobilization of patients, so the heart rate should be used in combination with other variables.
In upright exercise, the change in blood pressure is usually characterized by an initial increase in systolic blood pressure (SBP). As the exercise intensity increases, the systolic blood pressure further increases linearly, while the diastolic blood pressure tends to remain stable or slightly increase.18 Compared with the systolic or diastolic blood pressure, the mean arterial pressure can better reflect the blood flow state of the heart, brain, and kidneys.19 Therefore, mean arterial pressure and systolic blood pressure should be assessed before mobilization, and the fluctuation in blood pressure should be < 20%.
Additionally, the cardiac index can reflect cardiac pumping function and thus indirectly represents the cardiac reserve. Although some researchers use the cardiac index as an assessment variable, research data supporting its clinical importance are lacking. Therefore, the cardiac index can be used as a reference. The administration of vasoactive medications is not an absolute contraindication to mobilization, but changes in dosage and threshold dosage can indirectly reflect whether a patient’s hemodynamics are stable, which may have an impact on mobilization. However, previous expert consensus did not recommend the threshold dosage of vasoactive medications.8 This review found that low and medium maintenance dosages of single vasoactive medications do not hinder mobilization, and researchers mostly agree regarding the dosages of common medications (Table 2). Low and medium dosages of vasoactive drugs can maintain circulatory stability and prevent adverse events through vasoconstriction. Moreover, the dosage did not increase within 2 h before mobilization; thus, mobilization can be considered when the hemodynamics of a patient is relatively stable.
Classification of Vasoactive Medication Dosage
Respiratory Criteria
For patients on mechanical ventilation, respiratory reserve can affect their activity tolerance, which should be a focus. Some researchers believe that 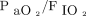 can accurately reflect oxygenation and the potential respiratory reserve. A value > 300 indicates a sufficient respiratory reserve, a value of 200–300 indicates a critical respiratory reserve, and a value < 200 indicates almost no respiratory reserve.17 Although
can accurately reflect oxygenation and the potential respiratory reserve. A value > 300 indicates a sufficient respiratory reserve, a value of 200–300 indicates a critical respiratory reserve, and a value < 200 indicates almost no respiratory reserve.17 Although 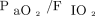 < 300 is not necessarily a contraindication to mobilization, it can prompt medical staff to pay attention to the balance of oxygen supply and consumption during mobilization. Therefore, this value is also recommended as an assessment variable.
< 300 is not necessarily a contraindication to mobilization, it can prompt medical staff to pay attention to the balance of oxygen supply and consumption during mobilization. Therefore, this value is also recommended as an assessment variable.  is not as sensitive as
is not as sensitive as  , but it can still reflect oxygenation. Because
, but it can still reflect oxygenation. Because 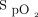 is convenient to measure, its utilization rate is currently higher than that of
is convenient to measure, its utilization rate is currently higher than that of 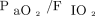 . If
. If 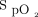 ≥ 88% and the recent fluctuation is < 4%, the patient can be considered to have a sufficient respiratory reserve. Mechanical ventilation is not a contraindication for mobilization and can provide respiratory support during mobilization, but the occurrence of patient-ventilator asynchrony should be prevented. Therefore, the selection of ventilator parameters and modes is important. Medical staff tend to provide patients with a certain degree of ventilation support and increase
≥ 88% and the recent fluctuation is < 4%, the patient can be considered to have a sufficient respiratory reserve. Mechanical ventilation is not a contraindication for mobilization and can provide respiratory support during mobilization, but the occurrence of patient-ventilator asynchrony should be prevented. Therefore, the selection of ventilator parameters and modes is important. Medical staff tend to provide patients with a certain degree of ventilation support and increase  by 0.2 for initial low-intensity activities; if the patient is tolerant, they can maintain and gradually reduce the level of ventilation support or promote higher-intensity activities with the same level of support. In addition, patients who are able to adapt to the autonomous breathing mode of ventilators may be more tolerant to active mobilization than those who cannot adapt.
by 0.2 for initial low-intensity activities; if the patient is tolerant, they can maintain and gradually reduce the level of ventilation support or promote higher-intensity activities with the same level of support. In addition, patients who are able to adapt to the autonomous breathing mode of ventilators may be more tolerant to active mobilization than those who cannot adapt.
Neurological Criteria
Vincent et al20 emphasized adequate analgesia and minimal sedation. Light sedation can promote the implementation of early mobilization as well as the rehabilitation of patients. The level of consciousness is an important condition in the evaluation of whether to initiate active mobilization. In addition to the patient’s underlying disease, consciousness is closely related to sedation. Although the extracted consciousness assessment parameters were inconsistent, all concerned light sedation. The Glasgow Coma Scale score is widely used in clinical practice but cannot truly represent the language score of patients on invasive mechanical ventilation. The 2018 Chinese Adult Analgesia and Sedation Guidelines recommend using the Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale and the Sedation-Agitation Scale scores as sedation assessment tools.21 Although additional evidence is needed to guide the assessment of consciousness, consciousness and the ability to follow simple instructions are basic requirements for active mobilization. Thus, many researchers include the standardized 5 questions for cooperation assessment in the sedation assessment to help judge whether patients can participate in active mobilization.
Musculoskeletal Criteria
Previous studies12,13 and expert consensus8 focused only on orthopedic assessment variables, such as unstable fractures that could affect mobilization, but not on the assessment of muscle strength. Active mobilization requires the active participation and cooperation of patients. Therefore, this systematic review considers muscle strength a key variable and combines this variable with orthopedic variables to form the musculoskeletal criteria. There are many contraindications in orthopedics that require patients to remain immobile. Although patients may be restricted to the bed, they can still perform active activities with healthy limbs to prevent muscle atrophy. Limb muscle strength is necessary for active mobilization, but the assessment of muscle strength has not been unified. Medical staff may believe that if patients can actively move their joints, they can begin active mobilization. When the upper limbs can resist gravity, patients can perform exercises involving the upper limbs, sitting up in the bed, and sitting in a chair; when the lower limbs can resist gravity, patients can exercise their lower limbs and gradually participate in bedside standing and walking training.
Other Criteria
Current evidence has indicated that mechanically ventilated patients with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation can participate in active mobilization.22,23 However, preventing any sudden changes in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during the activity is important. Continuous renal replacement therapy is not a contraindication for active mobilization, but the position of the intravenous catheter could be affected by an active range of motion, resulting in the failure of continuous renal replacement therapy.24 Therefore, additional high-quality evidence regarding active mobilization programs in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or continuous renal replacement therapy is required. In addition, parameters related to routine blood indexes have not been considered in previous studies12,13 or expert consensus.8 The oxygen content in the body is proportional to the level of hemoglobin, and an acute decrease in hemoglobin can indicate active or recent bleeding, particularly with hemodynamic instability.17 A decrease in the platelet count increases the risk of capillary injury and bleeding after activities and needs to be assessed. Activities also increase the risk of hypoglycemia, leading to a change in the level of consciousness of patients. Therefore, blood glucose levels should be assessed. Fever causes a stringent state in the body, and a patient may not have enough physical strength to tolerate mobilization. Therefore, patients with fever may be suitable for bed rest or moderate in-bed exercise during the acute phase.
Safety of Early Active Mobilization
No serious adverse events were reported in this systematic review, and the incidence of adverse events was ≤ 3%, which is lower than that reported in previous studies.12,13 Adverse events were mainly caused by insufficient cardiac and respiratory reserves and inadequate catheter protection. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment is the foundation of patient safety, and preparation for and implementation of mobilization are important. First, the surrounding environment should be kept clean and safe. The range of mobilization should be determined by indwelling catheters and related equipment. Important equipment should be in good condition. Moreover, accident prevention and treatment plans should be developed in advance. Second, the number of early mobilization team members should be sufficient. Stiller16 suggested that at least 2 medical personnel should attend to patients during activities. Our review suggests that the number of participants should be determined according to the approach of active mobilization. For in-bed activities, 1 or 2 medical personnel are sufficient, while for out-of-bed activities, at least 3 medical personnel are required: 1 or 2 to guide, assist, and monitor the patient; another to protect the artificial airway and ventilator tubes; and another to protect indwelling catheters. Therefore, additional guidance is expected to be proposed in future research to ensure patient safety during early mobilization and minimize the risk of adverse events.
Limitations
This study included only Chinese- and English-language articles, and publication bias may exist. Most included articles were of moderate quality. Some RCTs did not report randomization or allocation concealment. Although it is difficult to implement blinding in subjects and personnel in early mobilization, researchers should pay attention to the randomized assignment and blinding of outcome assessments to avoid selection or implementation bias. Although the subjects included in this study were in many types of ICUs, the research results and conclusions may not be applied to all clinical scenarios. While mechanical ventilation is a major risk factor for ICU-acquired weakness, there are other risk factors. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct targeted discussions regarding patients who are not mechanically ventilated with other risk factors and the clinical application of the safety assessment criteria to enable further optimization. In addition, only RCTs and cohort studies were included in this review, which may have affected the comprehensiveness of the safety assessment variables and specific parameters.
Conclusions
The safety assessment criteria for the early active mobilization of mechanically ventilated ICU patients include cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, musculoskeletal, and other criteria. Currently, the safety assessment variables reported in different articles are relatively consistent, but the selection of specific parameters differs. Whether the parameters are stable is important. The stability of the parameters can be more representative of a patient’s condition stability than the absolute values. Accordingly, we created flow diagram of recommended safety assessment criteria. A safety assessment should be initiated within 48–72 h after the patient is admitted to the ICU, and the patient needs to be reassessed before each mobilization. Through a focused assessment of the cardiac reserve, respiratory reserve, consciousness, and muscle strength combined with the patient’s condition, a personalized active mobilization protocol should be developed. However, only subjects who received mechanical ventilation were included in this study, and the final review included only RCTs and cohort studies. Therefore, the promotion of the safety assessment criteria may have some limitations, and the assessment requires further validation and optimization.
Footnotes
- Correspondence: Xiuni Gan RN, Department of Nursing, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China. E-mail: ganxn{at}163.com
The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary material related to this paper is available at http://www.rcjournal.com.
- Copyright © 2021 by Daedalus Enterprises